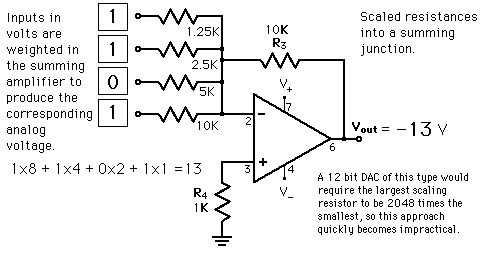
Four-Bit D/A Converter
One way to achieve D/A conversion is to use a summing amplifier.
Electronics concepts
Digital Circuits
Reference
Horowitz & Hill
Digital Systems, Sec 9-16.
| HyperPhysics*****Electricity and magnetism | R Nave |
Digital-to-Analog ConversionWhen data is in binary form, the 0's and 1's may be of several forms such as the TTL form where the logic zero may be a value up to 0.8 volts and the 1 may be a voltage from 2 to 5 volts. The data can be converted to clean digital form using gates which are designed to be on or off depending on the value of the incoming signal. Data in clean binary digital form can be converted to an analog form by using a summing amplifier. For example, a simple 4-bit D/A converter can be made with a four-input summing amplifier. More practical is the R-2R Network DAC.
|
Index Electronics concepts Digital Circuits | ||
|
Go Back |
Four-Bit D/A ConverterOne way to achieve D/A conversion is to use a summing amplifier.  |
Index Electronics concepts Digital Circuits Reference Horowitz & Hill Digital Systems, Sec 9-16. | ||
|
Go Back |
R-2R Ladder DAC
|
Index Electronics concepts Digital Circuits Reference Horowitz & Hill Sec 9-16. Tocci Digital Systems, Sec 10-3. Simpson Sec 15.2.3. | |||
|
Go Back |
R-2R Ladder DAC Details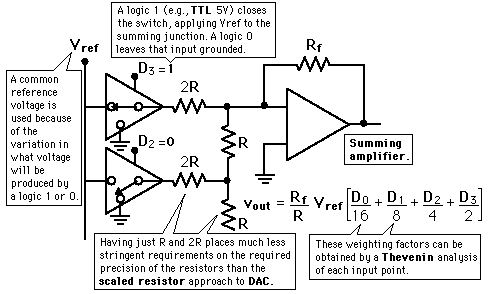
|
Index Electronics concepts Diode varieties Reference Horowitz & Hill Sec 9-16. Tocci Digital Systems, Sec 10-3. Simpson Sec 15.2.3. | ||||
|
Go Back |
Thevenin Example: R-2R Ladder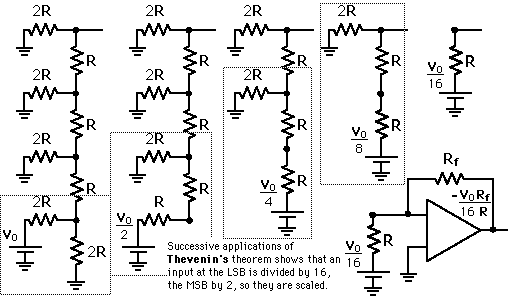
|
Index Electronics concepts Reference Simpson Sec 15.2.3. | ||
|
Go Back |